Fully continuous pyrolysis plant can achieve large-scale treatment of waste tires. The whole process of the fully continuous pyrolysis plant is completed in a closed equipment pipeline, which can effectively avoid dust, VOCs leakage and other problems. It effectively reduces pollution to the environment and makes it easier to meet environmental emission standards.
Compared with batch pyrolysis plant, continuous pyrolysis plant greatly improves production efficiency and can meet the treatment needs of a large number of waste tires and plastics. Fully automatic pyrolysis plant can precisely control parameters, such as pyrolysis temperature and residence time.
The process parameters of continuous pyrolysis equipment are relatively easy to control and can maintain a relatively stable operating state. The fully automatic tire pyrolysis process allows rubber to be more fully decomposed, thereby improving the quality of recycled oil and carbon black products.
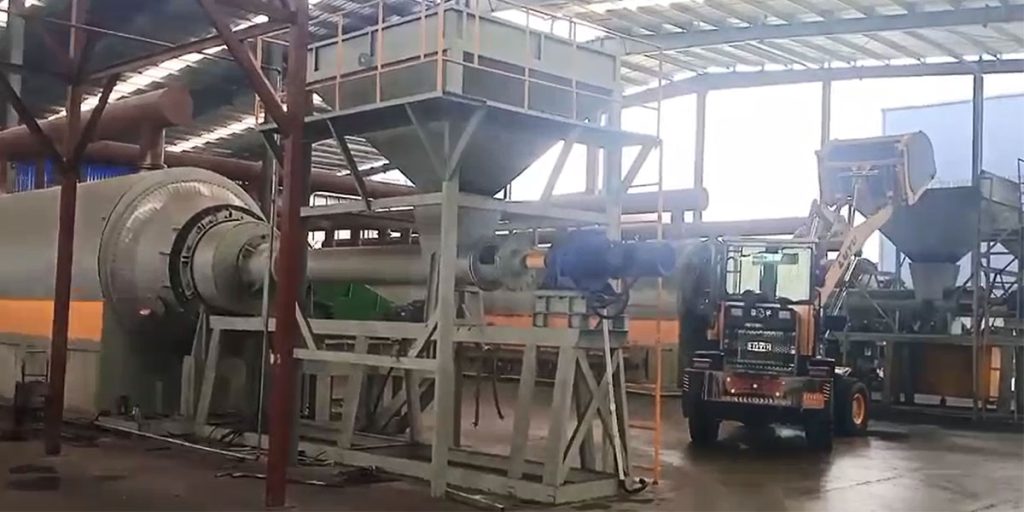

The fully automatic tyre pyrolysis plant can realize continuous feeding and continuous pyrolysis of waste tires, as well as continuous production of pyrolysis oil and carbon black in an oxygen-free or low-oxygen high-temperature environment.
The following is the continuous pyrolysis process of waste tires:
The pretreated waste tire rubber powder continuously enters the pyrolysis reactor through the feeding system. The feeding system needs to ensure sealing performance to prevent air from entering the pyrolysis reactor.
In the pyrolysis reactor, the tire particles undergo thermal decomposition reaction at high temperature (400-800℃). The high molecular polymers such as rubber and fiber in the tire are broken into smaller molecular chains to generate products such as fuel oil, carbon black and combustible gas.
The continuous pyrolysis reactor is the core equipment for the tyre continuous pyrolysis plant. It can provide stable heating conditions and suitable reaction space, allowing tire rubber powder to undergo pyrolysis reaction in an oxygen-free or oxygen-deficient environment.
The carbon black is discharged through the water-cooled spiral slag system. The discharging system must ensure that the pyrolysis products can be discharged smoothly, while also avoiding the leakage of hot gas and materials.
The pyrolysis products are separated by a separation device. Separation and collection equipment includes condensers, cyclone separators, filters, oil tanks, gas cabinets, etc. They are used to separate and collect pyrolysis products so that products in different states can be effectively recovered and utilized.
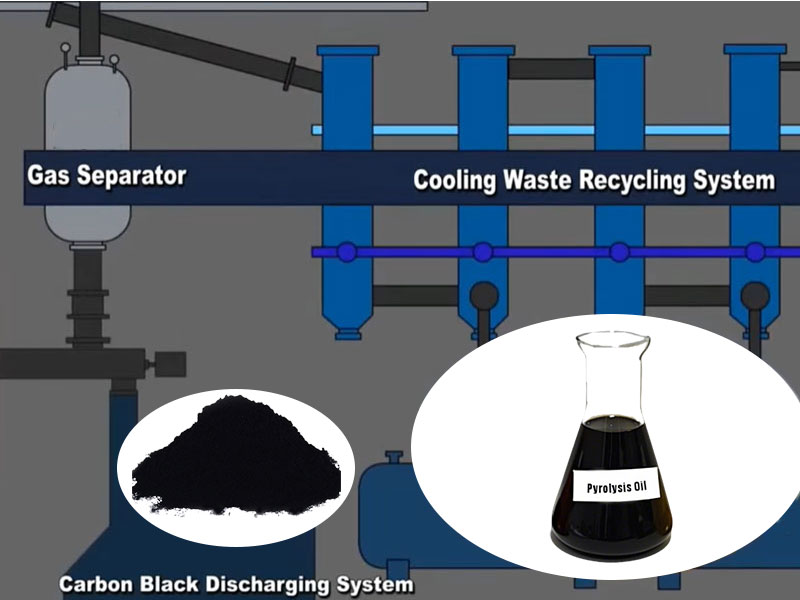
The fuel oil is collected in the pyrolysis oil tank through the condensation system. After purification, the non-condensable gas can be supplied to the burner of the heating system as fuel.
The temperature and atmosphere control system is used to accurately control the temperature and atmosphere conditions in the pyrolysis reactor. The power of the heating source is adjusted through the temperature sensor and controller to keep the pyrolysis temperature within the set range. At the same time, the oxygen-free or oxygen-deficient atmosphere in the reactor is maintained by controlling the intake volume and gas composition.
The tail gas treatment system includes activated carbon adsorption device, catalytic combustion device, bag filter, etc. They are used to treat the tail gas generated during the pyrolysis process, remove harmful substances in it, and meet environmental emission standards.
Continuous production: The continuous tyre pyrolysis process can achieve continuous feeding, continuous reaction and continuous discharging. The fully continuous pyrolysis plant has high production efficiency and can meet the needs of large-scale industrial production.
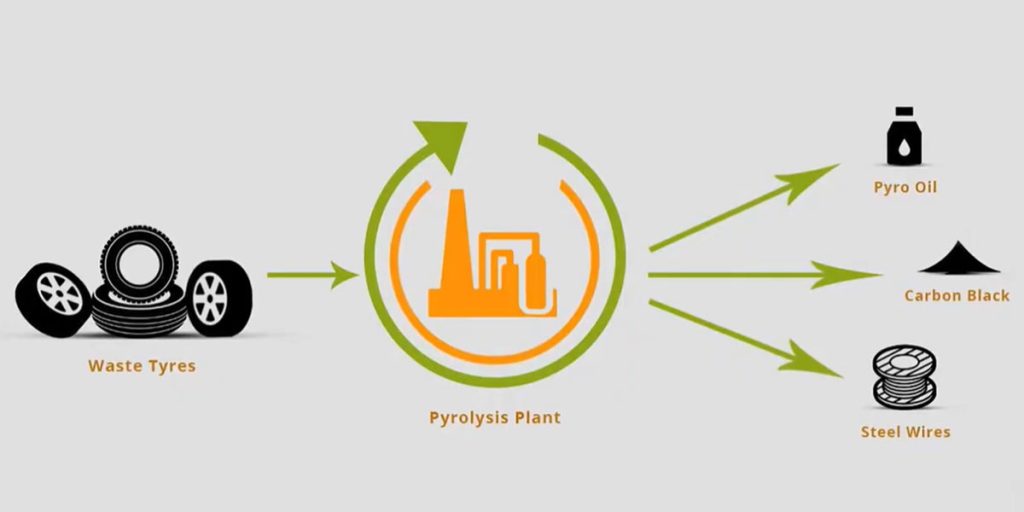
High resource utilization: Rubber, fiber, steel wire and other resources in waste tires can be fully recycled. Among them, fuel oil can be used as fuel or chemical raw materials, carbon black can be used as a reinforcing agent and filler for rubber products, and steel wire can be recycled and reprocessed, realizing the resource utilization of waste tires.
Good environmental performance: The waste tire pyrolysis process is carried out in an oxygen-free or low-oxygen environment, avoiding the emission of harmful gases during the combustion process, such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, dioxins, etc. At the same time, the fully continuous pyrolysis plant is equipped with an efficient exhaust gas treatment device, which can remove pollutants in the exhaust gas and meet environmental emission standards.
High degree of automation: The continuous pyrolysis plant adopts an automated control system to accurately control each link, such as feeding, heating, reaction, and product separation. This improves the stability and reliability of the tyre pyrolysis recycling process and reduces manual operation and labor intensity.

The tire pyrolysis industry has made steady progress in 2024. Europe in particular has seen a series of commercial and technological achievements this year.
List of major waste tire pyrolysis projects announced in 2024:
2024-12-17, Pyrum Innovation AG expects to break ground on its End-of-Life Tires (ELT) pyrolysis plant in Germany in spring 2025, having largely completed the various approvals required for the plant.
November 12, 2024, Hankook Tire Co., Ltd. began mass production of tires using three ISCC+ certified carbon black products extracted from waste tires. The carbon blacks are produced using waste tire pyrolysis oil (TPO).
October 31, 2024, Bolder Industries' NextGen thermal tire reuse project was selected along with a number of other sustainability-related candidate projects to receive €4.8 billion in EU development funding.
October 10, 2024, Pyrum Innovation's plant in Dillingen/Saarland, Germany, completed the first trial run of the new recycling line, reaching design capacity. It has received an "unlimited supply license" from Continental AG, and rCB can be supplied by its recently expanded plant.

September 5, 2024 Marubeni Corporation plans to develop a business model for tire recycling supply chains in Japan, Southeast Asia and other regions. And invest in the "Green Rubber Energy" of Thailand's waste tire pyrolysis company to produce rCB and tire pyrolysis oil.
September 4, 2024, Scanship, a subsidiary of Norwegian environmental technology group Vow ASA, and British tire recycler Murfits signed an agreement to jointly promote the development of waste tire pyrolysis technology. They signed a preliminary engineering design (FEED) contract for the design and construction of a "large-scale" pyrolysis plant, which will be put into operation in 2026.
On September 3, 2024, Bridgestone EMEA, BB&G Group and Versalis jointly studied technical solutions for the "large-scale" use of thermoplastic polyolefins in tire rubber production.
On August 20, 2024, Scandinavian Enviro Systems increased its stake in the waste tire pyrolysis joint venture with Antin Infrastructure. The company is also supported by Michelin.
On August 20, 2024, Neste strengthened the logistics infrastructure of the Porvoo refinery to support the expansion of chemical recycling operations for liquid waste, including pyrolysis oil produced from End-of-Life Tires (ELT).

On July 8, 2024, Swedish Enviro received an order from a major European oil company for the delivery of 500 tons of pyrolysis oil recycled from waste tires.
On July 3, 2024, Norway's Wastefront AS supplied aviation fuel made from waste tire pyrolysis oil from a €120 million plant. The waste tire pyrolysis plant is designed to process 10 million waste tires per year and will be put into operation in 2026.
On June 18, 2024, South Korea's LD Carbon Black completed a €26 million financing led by Toyota to expand the current 70 million tons per year rCB plant and signed a 10-year waste tire pyrolysis oil (TPO) supply agreement with SK Incheon Petrochemical.
On May 21, 2024, the UK's Circular Technology Group (Circtec) received €150 million in funding to build the "largest" waste tyre pyrolysis plant in Europe. In addition, on May 17, a project costing 285 million euros and processing 20,000 tons of waste tires per year broke ground, with major investors including BP and Birla Carbon.
On May 13, 2024, Orilon Engineering Carbon invested in Alpha Carbone, a waste tire recycler headquartered in Toulouse, France. It will expand its tire pyrolysis business worth 10 million euros to an annual processing capacity of 16,000 tons of waste tires.
On May 10, 2024, Continental Carbon Black plans to build a large rCB plant. It is expected to be put into production in 2026/annual production of 30,000 tons of rCB, 35,000 tons of TPO, and 2,300 tons of steel wire.
On April 19, 2024, Swedish Invero signed an agreement with Swedish Tire Recycling to provide raw materials to the waste tire pyrolysis plant under construction.
On March 8, 2024, German Perrom Innovation reached a cooperation agreement with GreenTech Recycling Tires AB. The construction of a tire recycling plant with an annual processing capacity of 20,000 tons of End-of-Life Tires (ELT) is scheduled to be put into production in 2027.
On February 22, 2024, L4T Group invested 42 million euros to build a plant on a 10-acre land in the bonded area of the South Louisiana Port. It converts End-of-Life Tires/Tyres (ELT) into products such as advanced biofuel feedstock, recycled carbon black and scrap steel.

An Australian general waste and tire recycling authoritative body turned to Environment Minister Sussan Ley in November last year with a request to prohibit whole bale tire…

Aliapur – a French end-of-life tire management authority – recently announced a call for applications to participate in a tender to renew end-of-life tire collection and recycling contacts for 2021–2024..