The plastic pyrolysis process uses chemical recycling to process waste plastics. The main components of waste plastics are high molecular polymers (polyethylene PE, polypropylene PP, polystyrene PS). Plastic pyrolysis plant decomposes plastic waste thermally under oxygen-free conditions, converting it into valuable products such as fuel oil, syngas, and carbon black.
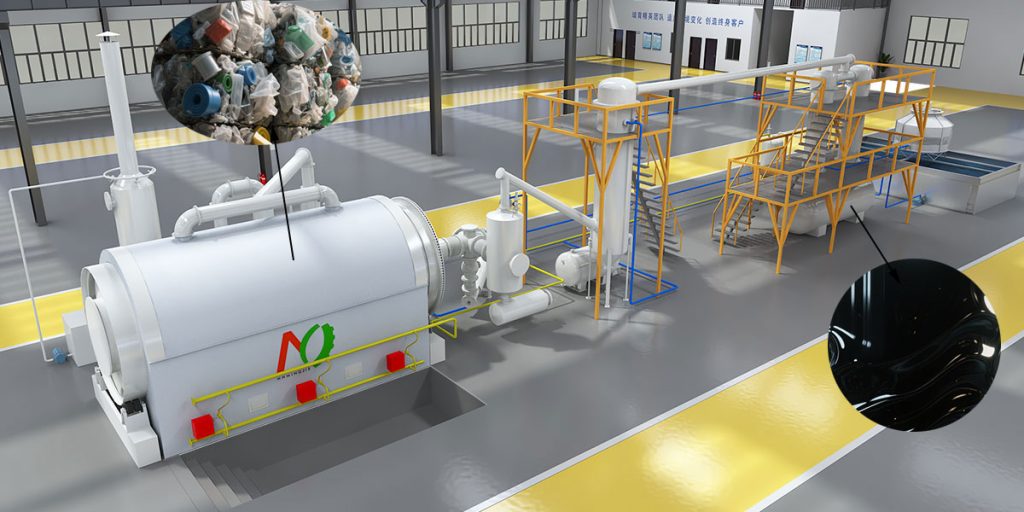

To address the plastic waste problem, various methods have been explored, including landfilling, incineration, and mechanical recycling.
While landfill disposal is simple and easy, it consumes significant land resources. Furthermore, plastic waste persists in landfills and can produce hazardous substances, polluting soil and groundwater.
Incineration can effectively reduce the volume of plastic waste, but the process produces large amounts of harmful gases, such as dioxins and furans. These gases seriously affect air quality and harm human health.
While mechanical recycling can reprocess some plastics, it is limited by factors such as the type of plastic and impurities. The quality of recycled plastic is often inferior to virgin plastic, and it can only be recycled a limited number of times. Ultimately, a large amount of unrecyclable plastic waste is generated.
The pyrolysis chemical recycling offers a new approach and solution to the plastic waste problem, becoming a novel plastic waste treatment technology. Plastic pyrolysis is a chemical recycling technology that converts waste plastics into small-molecule chemicals through a high-temperature, anaerobic, or anoxic thermal decomposition reaction.
Unlike mechanical recycling, batch pyrolysis plant can process mixed, heavily contaminated, or difficult-to-process plastics, making it an important supplementary means of addressing “white pollution.”
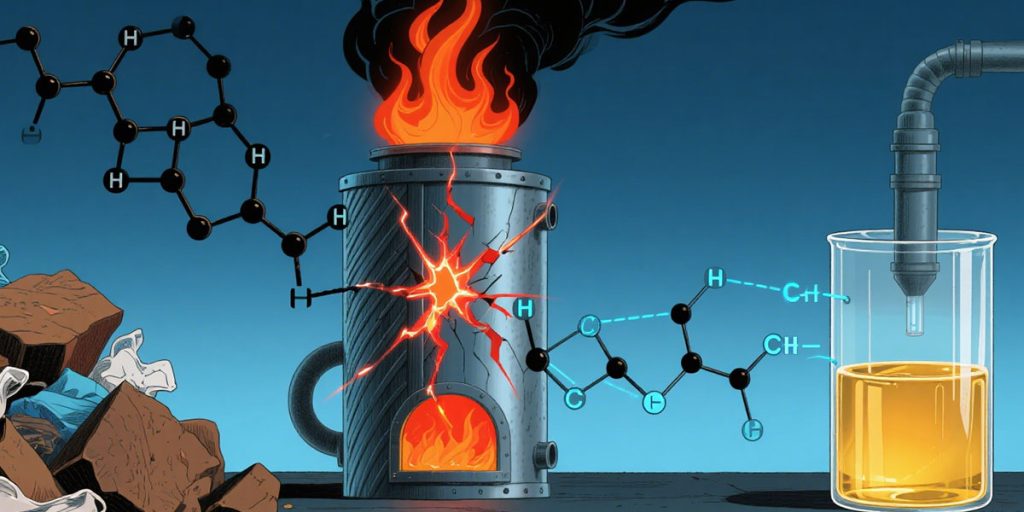
Plastic pyrolysis refers to the process of using heat in an oxygen-free or low-oxygen environment to break the chemical bonds within long-chain plastic molecules, allowing them to recombine into smaller compounds. The plastic pyrolysis process is like breaking a long, complex molecular chain into smaller components, which are then reassembled into new, simpler structures.
At a molecular level, plastics are composed of polymers. These polymers are composed of a large number of repeating units linked by covalent bonds, forming a long, chain-like molecular structure.
Take common polyethylene (PE) pyrolysis as an example. It is made from the monomer ethylene, and its molecular structure contains numerous carbon-carbon (C-C) and carbon-hydrogen (C-H) bonds. During the pyrolysis process, when sufficient heat is applied, these chemical bonds absorb energy, become unstable, and eventually break.
C-C bond cleavage is a key step in the plastic pyrolysis process, as it directly leads to the decomposition of the polymer. As C-C bonds break, the long-chain molecules are broken into shorter fragments. These fragments further react to produce various small-molecule compounds, such as hydrocarbons, hydrogen, and carbon monoxide.

The plastic pyrolysis process can be roughly divided into three stages, each accompanied by distinct physical and chemical changes.
The drying stage primarily removes moisture and low-boiling-point impurities from the plastic. This stage is crucial, as moisture can interfere with the pyrolysis reaction, potentially leading to energy waste and reduced product quality.
As the temperature gradually rises, the pyrolysis stage begins, where high-molecular-weight polymers begin to undergo cracking reactions. As the temperature rises further, the pyrolysis reaction intensifies, producing a greater variety and quantity of small-molecule products.
In the plastic pyrolysis plant, different types of plastics exhibit varying pyrolysis behavior and product distribution. Polyethylene primarily produces various hydrocarbon compounds during pyrolysis, including alkanes and alkenes. The carbon chain length and degree of saturation of these hydrocarbons vary with pyrolysis conditions.
Finally, the cooling stage cools the high-temperature gaseous products produced by pyrolysis. Some of these gaseous substances condense into liquid, forming pyrolysis oil. The uncondensed gases become pyrolysis gas.

An Australian general waste and tire recycling authoritative body turned to Environment Minister Sussan Ley in November last year with a request to prohibit whole bale tire…

Aliapur – a French end-of-life tire management authority – recently announced a call for applications to participate in a tender to renew end-of-life tire collection and recycling contacts for 2021–2024..